9. What are XYZ Files?#
The XYZ file format is a text-file format. Unlike PDB files, there is no formal standard and several variations exist. However, a typical XYZ format specifies the molecule geometry by giving the number of atoms with Cartesian coordinates that will be read on the first line, a comment on the second, and the lines of atomic coordinates in the following lines.
Typically, we use these files to store molecular geometries in Quantum Mechanical (QM) calculations. These files generally contain up to a few hundred atoms. For example, let’s build the small molecule alanine dipeptide, and store this data in .xyz.
9.1. Example with Alanine Dipeptide#
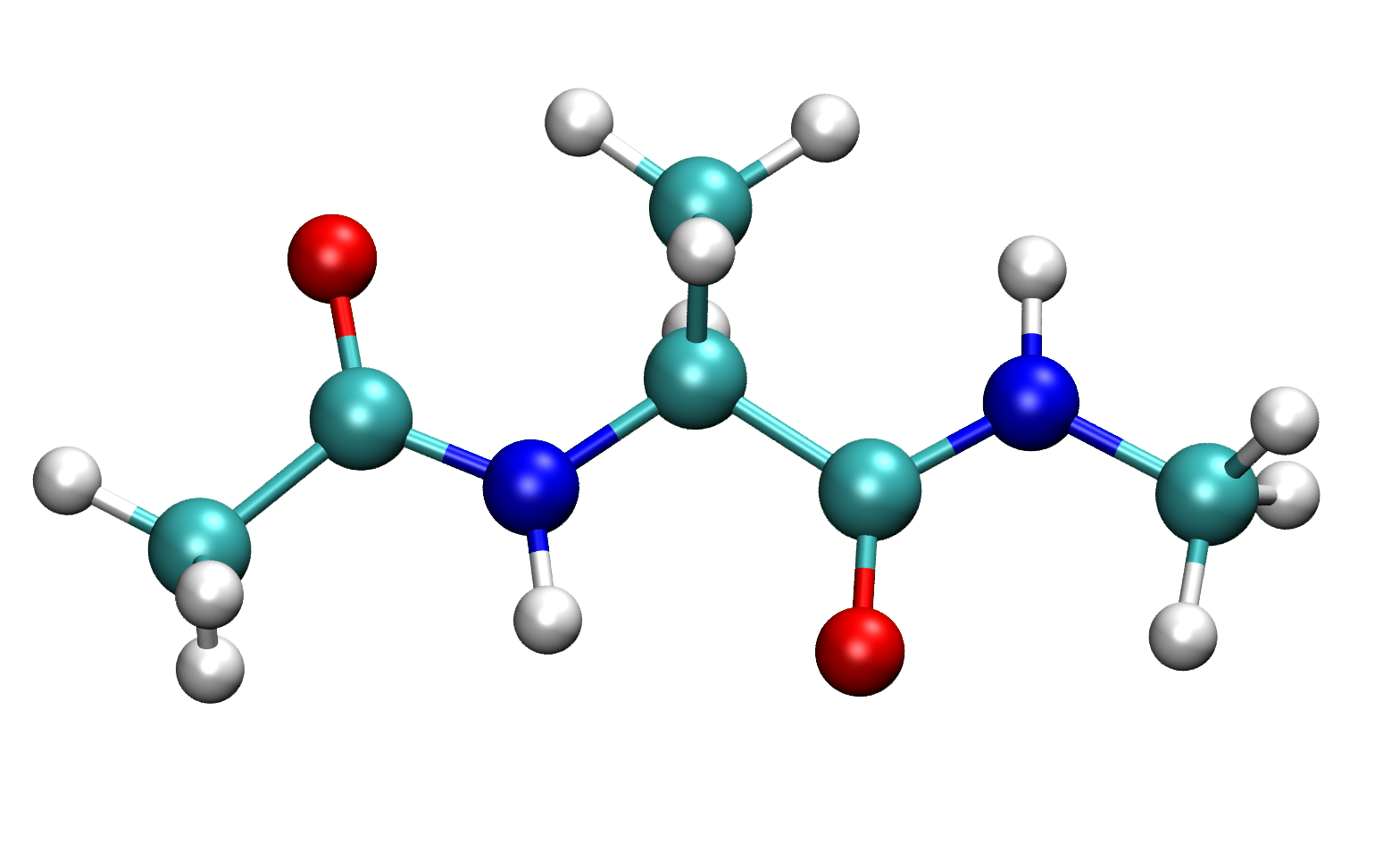
Alanine dipeptide is the amino acid, Alanine, with the N-/C-terminal capped by an N-acetyl and N′-methylamide to neutralize the charges. First we will build alanine dipeptide via IQmol, then save the structure as ala.xyz:
Open up the software, IQmol
Use your mouse/trackpad and click any area on the screen
Starting with the first Carbon atom, add the rest of the atoms, ignoring hydrogen
Click on the ‘C’ to get the periodic table
Click on Nitrogen, and replace the appropriate Carbons
Repeat step 5. but with Oxygen
Click on the
add hydrogensbuttonClick on the
minimize energybuttonSave the structure as
ala.xyzto your desired location (I saved them to my~/Desktop/)
9.2. Open the ala.xyz File#
First, open your terminal, and then change directories to where you saved the ala.xyz. Since I saved them to my ~/Desktop/, I will cd there, and use less to view ala.xyz:
cd ~/Desktop/
less ala.xyz
You should see something like this:
122
2
3C -4.63266 -0.12314 -0.02867
4C -3.47843 0.78724 -0.33464
5N -2.20323 0.42630 -0.00959
6C -1.04137 1.27430 -0.28628
7C 0.27575 0.55742 0.00041
8N 1.45796 1.17048 -0.29496
9C 2.75416 0.56631 -0.05757
10O 0.27431 -0.56825 0.48031
11O -3.70495 1.85032 -0.89391
12C -1.11255 2.56299 0.55432
13H -4.29553 -1.05515 0.47169
14H -5.15086 -0.39580 -0.97185
15H -5.34808 0.39806 0.64145
16H -2.06950 -0.49744 0.42698
17H -1.04318 1.52892 -1.36918
18H 1.44851 2.11097 -0.71632
19H 2.67618 -0.44502 0.39384
20H 3.33886 1.21183 0.63059
21H 3.30037 0.47916 -1.01990
22H -2.03263 3.14107 0.33971
23H -0.25509 3.23182 0.33529
24H -1.10019 2.31238 1.63679
Explanations:
The first line of
ala.xyzis the total number of atoms.The second line is reserved for comments, so you can include details about the structure here
The rest of the file contains the elemental symbol, followed by x-,y-z- coodinates
Simple yeah?
9.3. Additional Resources#
For more information, please refer to the following resource:
RCSB: Guide to Understanding PDB data
“The primary information stored in the PDB archive consists of coordinate files for biological molecules. These files list the atoms in each protein, and their 3D location in space. These files are available in several formats (PDB, mmCIF, XML). A typical PDB formatted file includes a large “header” section of text that summarizes the protein, citation information, and the details of the structure solution, followed by the sequence and a long list of the atoms and their coordinates. The archive also contains the experimental observations that are used to determine these atomic coordinates.”